What Are the Key Characteristics of FR1 Bands?
As 5G networks expand globally, understanding the technical specifications and advantages of Frequency Range 1 (FR1) bands is essential for anyone involved in network planning, policy making, or simply keeping up with telecommunications advancements. FR1 bands cover lower frequencies compared to the high-frequency millimeter waves of FR2, playing a critical role in achieving comprehensive network coverage and reliable connectivity.
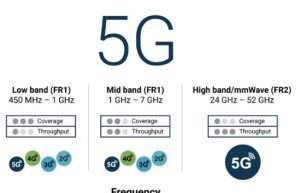
Frequency Range and Allocation
FR1 bands encompass frequencies from 450 MHz up to 6 GHz. This range is strategically important because it includes many of the frequencies already used by previous generations of mobile networks, such as 4G LTE. Key bands within the FR1 range include:
- n1 (2100 MHz)
- n3 (1800 MHz)
- n5 (850 MHz)
- n7 (2600 MHz)
- n28 (700 MHz)
These bands are widely adopted for 5G deployment due to their optimal balance between coverage and capacity. They are particularly effective in areas where signal reach and penetration into buildings are paramount.
Coverage Capabilities
One of the standout features of FR1 is its excellent coverage. Lower frequency waves, which FR1 utilizes, have the natural advantage of longer wavelengths that travel greater distances and penetrate obstacles more effectively than higher frequency waves. This characteristic makes FR1 ideal for covering large geographic areas and providing indoor coverage, which is crucial for consistent user experience across different environments.
Balanced Capacity and Speed
While FR1 may not provide the ultra-high speeds associated with FR2’s millimeter waves, it still offers significant improvements over previous generations. Typical speeds in FR1 bands can range from 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps under good conditions. This range is sufficient for most current applications, including streaming high-definition video, seamless web browsing, and responsive cloud services.
Compatibility and Cost-Effectiveness
The use of FR1 bands allows for better integration with existing telecommunications infrastructure. Many areas already equipped with 4G LTE technology can be upgraded to 5G using the same frequency bands, which helps reduce the costs and complexities associated with deploying new antennas and towers.
Additionally, devices operating in the FR1 spectrum generally require less power for signal transmission, which can lead to longer battery life and lower energy consumption overall.
Strategic Importance for Widespread 5G Adoption
The role of FR1 bands in the global rollout of 5G cannot be overstated. Their ability to provide widespread coverage and penetrate buildings effectively makes them fundamental to achieving near-universal 5G connectivity, particularly in rural and suburban areas where higher frequency bands might not be practical due to their limited range and penetration capabilities.
In conclusion, the FR1 bands are critical to the successful deployment and operation of 5G networks around the world. They offer the necessary blend of coverage, capacity, and cost-effectiveness that will continue to support a wide range of mobile services and pave the way for new technological advancements. As the 5G landscape evolves, the strategic deployment of FR1 will remain a cornerstone of global connectivity strategies.